Payroll Outsourcing & Management Services
Salary Structuring
Payroll compliance is in actual a legal framework to which companies or organisations must adhere. Statutory compliance means the treatment of workers or employees. Most of the company’s money and time goes into safeguarding compliance with these laws. Everything from being compliant to the minimum wages paid to maternity benefits to provident funds needs a lot of time and experts who can advise on all of these compliance measures. Therefore, the companies dealing with payroll compliance need to be well-versed with India’s different labour laws or labour regulations.

Choose among our Payroll Offerings:
Payroll explained like Chapter 101
Payroll is the list of employees who works for the company either in their own office or in someone else’s office. But they get paid by the company, for example. Paul is on the payroll of Apple, but if Facebook needs few IT Experts, Apple can send their employee to Facebook’s office to work for a contract period. Payroll is the total of money the employer pays to the employees. As a business function, it involves:
- Developing organization pay policy including flexible benefits, leave encashment policy, etc.
- Defining payslip components like basic, variable pay, HRA, and LTA
- Gathering other payroll inputs (e.g., the organization’s food vendor may supply information about the amount to be recovered from the employees for meals consumed)
- The actual calculation of gross salary, statutory as well as non-statutory deductions, and arriving at the net pay
- Releasing employee salary
- Depositing dues like TDS, PF, ESI etc. with appropriate authorities and filing returns
In short, we can say that the payroll process involves arriving at what is due to the employees, also called ‘net pay’, after deducting taxes.
Net pay = Income- Deduction,
Income = All regular income + allowances
What are the various Stages in Payroll ?
Payroll is an ever-going process with concurrent events at every place. The official performing this needs careful planning. Bank reconciliation is done to monitor actual deposits and accruals in withholdings, and contribution is a must. The Three-step process consists of pre-payroll, actual payroll and posts payroll activities.

Pre-Payroll Activities
Defining payroll policy
The net amount to be paid to any employee is calculated after considering the company’s various policies, such as HR Allowance, Dearness Allowance, Travelling Allowance, Casual leave and sick leave benefits, attendance policy, etc., play at that time. As a first step, such policies need to be well defined and approved by the management to ensure standard payroll processing.
Gathering inputs
The payroll process involves interaction with Finance departments, accounts department, so that alteration in wages and salary are taken into consideration immediately
In smaller organizations, we receive inputs from small teams. In larger companies, the data amount looks overwhelming. If you use intelligent payroll software with integrated features like leave and attendance management, employee self-service portal, etc., the inputs collection process does not remain a problem.
Reporting
Once the payroll calculation is complete for a month, you must get it approved from either C.F.O. or C.E.O. Try tp make report in detailed format such as department wise employee cost, location wise employee cost, etc. As a payroll officer, it becomes your responsibility to dig into the data, extract the required information, and share the reports.
Post-Payroll Process
Statutory compliance
Payroll accounting
Each Company keeps a record of all its financial transactions. Salary paid is one of the highest operational expense which is reported in the books of accounts. Therefore, it is essential to check that all wage and reimbursement data is fed accurately into the accounting/ERP system as part of payroll management.
Payout
Salary payments are done mostly by account transfers such as either NEFT or RTGS. Few of the organizations also issue cheques. While wages to labor are mainly done by cash payments. Large Companies provide better facilities as provide their employees with salary account in some leading banks. Once the calculation are done, you can make the payment of salary by a single click now. This statement consists of particulars like employee id, bank account number, amount of wages, etc. If you opt for payroll software with an employee self-service portal, you can easily publish the payslips and have your account and access the payslips.
What is the statutory compliance in payroll?
When you prepare payroll, being statutory compliant means paying as per the applicable employment norms set by the central and state legislation. Provision for minimum wages, payment of overtime wages to workers, TDS deduction, Provident fund, ESI are some statutory requirements that apply to Indian businesses.
While computing salary, you need to consider all these deductions and contributions. Income tax is one such deduction. Therefore, at the beginning of the year, the employee should make a declaration about his additional incomes, tax-saving investments, etc., called an ‘income tax declaration.’ Accordingly, We calculate an employee’s tax liability and deduct his TDS.
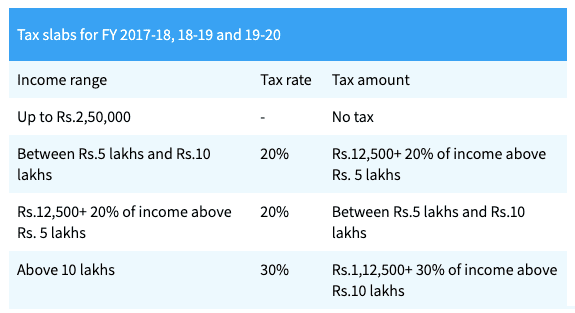
Based on the above tax slabs, you can calculate monthly tax liability and deduct TDS. The TDS is then deposited monthly with the government, and a quarterly report of all deductions are filed. Once you complete TDS returns for the fourth quarter, you can issue form 16 to employees. The employees use this form 16 as proof of tax deducted when filing their individual income tax return.
Non-adherence to the statutory law can lead to hefty fines and penalties. That is why you need to be up to date on all tax and payroll statutory changes.
What are the challenges in handling Payroll management process?
The payroll process becomes challenging due to two main reasons.
We have already discussed about non-adherence to statutory laws can lead to a levy of fines and penalties. There are cases, which may even threaten the existence of the business. However, today there is some advanced payroll management software that automatically processes payroll according to statutory laws.
Dependence on multiple payroll inputs sourcesBefore you process the payroll, you need to get all the data together from sources such as attendance register, conveyance facility availed record, data from HR team like salary revision information, etc., making it a complicated process. For many years HR and payroll officers were managing payroll on excel sheets. Still, excel sheets have problems like dependency on excel formulas for salary calculation, complexity in adding and removing employees and other limitations like manual data entry, difficulty in extracting information, etc.
What are the methods available for Payroll management?
Excel based Payroll management
Many businesses that are at an initial stage of operations and have a handful of employees go for excel based payroll management. Excel-based payroll management involves doing payroll calculation on excel sheets using a standard payroll calculation template. The mathematical formulas concepts used by the payroll officer for computation. Just because this method does not involve any cost, but it has its inherent limitations like
👉 High chances of clerical and mathematical with manual data entry.
👉 Managing payroll of list of employee is a tough task here, mainly adding and removing of employees from the list
👉 Cases of duplicate data entry or omission of value/entry is common.
👉 Updation of tax and other norms is often neglected or delayed.
Payroll Outsourcing
Outsourcing payroll is the best option that an organization have. Outsourcing means you want an external expert agency to take care of your day-to-day payroll function. Many organizations that need an error-free solution for payroll go for this option. Based on their pay cycle, every month, they provide employee salary information and other data such as attendance, leaves, reimbursement details, etc., to the payroll service provider. The service provider then computes payroll and also takes care of statutory compliance. However, since payroll is a crucial function and businesses want full transparency and control over it, they often hesitate to outsource payroll.
Payroll Software
As discussed above, you need to ensure that payroll inputs are coming from every source in a timely and seamless manner for running successful payroll. The intent of using software is to reduce the friction in getting the inputs. There is advanced payroll management software available in the market that automates payroll computation and serves as a holistic leave and attendance management, HR management, and employee self-service portal. Depending on your business size and use cases, you can opt for appropriate payroll software for your business.
Integration with time, attendance and leave management system
Time Management
Typically this module is used to track time spent on projects or specific activities. Consulting firms such as audit firms, specialist doctors, etc., who manage critical projects require a robust time management module for tracking time, and at times this data may also be used for billing clients.
Integration with the accounting system
Your accounting/ERP system needs to record every financial transaction, including payroll information like department wise employee cost, individual payroll components like reimbursements, tax due and paid, etc. Some payroll software integrates with accounting software via API( a way to push data directly from one software to another).
If the integration is not proper, the payroll officer needs to provide all transaction details to the accounts department. The accountant then manually posts it in journal entries in accounting/ERP software like Tally ERP, SAP, Quickbooks, etc. These integrations can help the finance and payroll team work together and avoid any manual entry of data.
Attendance
While most small organisation go for a manual attendance system, medium and large organisations have started using intelligent, automated tools such as biometric method, auto-tracking via system log-in, access cards, iris capture, etc. The data stored in a system linked to the payroll software that uses this data to calculate attendance days, overtime, etc. For seamless payroll processing, check that software supports attendance management and is configurable with access control machines.
Leave Management
Employees take a certain number of leaves in every organization, such as privilege or annual leave, casual leave, sick leave, holiday, etc. Employees are entitled to this leave in almost every organization.
If the software has leave management feature such as casual leave, sick leave, HR can credit these leaves to eligible employee account. So, the employee can apply for leave through the system. A sound plan should also define a workflow to notify the employee’s manager for either approval or rejection. Robust payroll software with a built-in leave management feature can help attain accurate payroll.
Tax Registrations for Above
- Organization Adhering to Minimum Wages
Minimum Wages Act, 1948, has issued guidelines about Minimum Wages. Both the Central Government and the State Government gives minimum wage rates. The wage rates vary from the employment, sector, and type of employee.
According to this act, the employer is responsible for paying wages at least every month on a timely basis. The wage period is fixed according to the employer’s convenience on a daily, weekly or monthly basis.
- Registration of company for (EPF) Provident Fund
The Provident Fund allows the employees to save some part of their income. The Provident Fund is an amount of funds accumulated through regular and monthly contributions made by employees and their employers.According to EPFO (Employee Provident Fund Organisation) rules and regulations, any company with 20 or more employees should register for Provident Fund. If the company fails to comply with EPFO rules and regulations, it is heavily penalised.
- Registration of Company for ESIC
The ESIC social security scheme brings affordable healthcare to employees and their family members. As per the ESIC Act, all companies with more than 20 employees whose monthly salary falls under Rs.21,000 should register under the Act.
So, if the company falls under the ESIC Act compliance, then the Employees CTC needs to be updated, including the ESIC employer and employee contribution.
- Including Gratuity in Employee CTC
According to the Payment of the Gratuity Act, 1972, Gratuity applies to all the establishments such as NGO’s, hospitals and educational institutions with ten or more employees. As Gratuity is a fixed contribution from the company’s side is part of the CTC. Thus, making Gratuity part of the employees CTC is mandatory.
EPI-ESI Filing
EPF Compliance-PF Return Filing
Provident fund has the sole purpose of encouraging savings among employees to benefit them during their retirement. It is a social security system introduced for the employer and the employee to make monthly contributions. Provident Fund contributions can only be withdrawn by the employee at the time of his/her retirement, barring a few exceptions. All employers having PF registration are responsible for filing returns monthly. The Provident fund return filing must be done on or before the 25th of every month. Here we have explained the filing of provident fund returns and the various forms through which the purpose must be fulfilled. Employers can now easily file PF returns through the Unified Portal. PF returns must be filed every month by employers having PF registration in India.
Service Covered
- Preparation of Salary/Wages Register
- Bulk PAN Verification
- Challan Verification
- Online Challan Generation and Submission
- Filing of EPF Return
Who should Buy
Businesses liable to file EPF Compliances
How It’s Done
- Purchase of plan
- FIll in the details in the template provided
- Upload documents on vault
- Return form prepared by Tax Expert
- Filed by Our Experts
Documents Required
- Salary Details of Employees/Labours
- Details of Employer
- Details of responsible person
- Challan details
What is the Employee Provident Fund (EPF)?
Employee Provident Fund (EPF) is a benefit for the employee during retirement. It is a social security fund created for the purpose of providing financial security and stability during retirement.
Applicability:
- Every specified factory or establishment in which 20 or more persons are employed. With the amendment in the rule of EPF, the limit of the minimum employee is 10 employee.
- Any factory or Establishment can also willingly cover under the Act, even if the number of employees is less than 20.
Eligibility:
Any person who is employed for work of an establishment or employed by the contractor in or in connection with the work of an establishment and drawing salary up to Rs.15,000/- p.m. The salary is calculated as Basic Salary plus Daily Allowance.
Rates of Contribution:
- Employer – 12%
- Employee – 12%
- – 1.16% to Central Govt.
Insurance Scheme:
All members contributing to Provident Fund are automatically insured for their life during the Service. Employer’s Contribution to the Insurance Scheme is 0.5%. The maximum amount payable to the nominee in case of death of an employee is Rs.100000/-
Pension Fund:
All employees covered under the Provident Fund become members of the Pension Scheme. 8.33% of Basic Salary up to Rs.15,000/- is contributed to the Pension Scheme from employers share of contribution. A minimum period of ten years of contributory service is required to be eligible to receive monthly Pension. The full pension is payable on completion of 20 years of contributory service.
Compliance Checklist under the EPF Act
| S.No. | Provisions | Compliance |
| 1 | Employer and Employee’s PF dues | 15th of the following month |
| 2 | Payment of Pension Fund | 15th of the following month |
| 3 | Payment of Insurance Fund | 15th of the following month |
| 4 | Detail of employees | Detail of employees enrolled as members PF fund, within 1 month of coverage in the prescribed form |
| 5 | Nomination Form | Immediately on Joining the fund in the prescribed form |
| 6 | Addition of members | Detail of newly enrolled members within 15 Days of the following month in the prescribed form |
| 7 | Deletion of member | Detail of members left service during the monthbefore21st of the following month in the prescribed form |
| 8 | Details of contribution | Detail of employees and employer’s contribution by 25th of the following month in the prescribed form |
| 9 | Detail of wages and contribution | For each member details shall be given By 30th April every year |
| 10 | Yearly Consolidated statement of contribution | To be forwarded yearly along with Form 3A |
| 11 | Return of ownership of the establishment | Within 15 days on coverage and whenever there is a change in ownership |
| 12 | Transfer of PF | Form 13 needs to file |
In addition to above Compliance related Insurance and pension also need to duly comply with.
Withdrawal rules under EPF Act
- The funds from an EPF account can be withdrawn completely in full settlements on attaining 58 years of age or at the time of retirement the employee can claim for a complete settlement or if an employee remains unemployed for a period of 2 months or more or in the case of death while in service before attaining the age of retirement, in which case the nominees or legal heirs are entitled to withdraw the accumulated fund.
- The partial withdrawal of funds from the EPF is available for educational opportunity, medical treatment, repayment of home loan, marriage, purchase of land/house/flat, in case the establishment/factory is closed, natural calamity, an year before retirement and unemployment for a period of more than one month.
Penalties on Non-Compliance to EPF Act
- Penalty of 12% per year interest for each day of delay in payment of contribution
- Penalty on late payment as mentioned:
- Delay up to 2 months: 5% interest p.a.
- Delay of 2-4 months: 10% interest p.a.
- Delay of 4-6 months: 15% interest p.a.
- Delay of more than 6 months: 25% interest p.a. not exceeding 100% at a time
Benefits of EPF
The employees covered under the various schemes of the Act are entitled for the following benefits
- Employees can take advances or make withdrawals*.
- PF amount of a deceased member is payable to the nominees or legal heirs.
- The employer not only contributes towards the PF but also makes the necessary contributions towards the employee’s pension which can be used by the employee post-retirement
- Under the EDLI Scheme employees are properly insured in order to avail the lump sum benefit at the time of death while in service.
- EEE (Exempt, Exempt, Exempt) tax benefit under the Income Tax Act enables tax-free returns for the employees.
- Employees receive special benefits in the form of added income to their savings in the form of interest.
- PF account can be transferrable if any member changes employment from one establishment to another where such Provident Fund scheme is applicable.
Professional Tax
Professional Tax Registration & Compliance Filing
Professional Tax is a tax levied on professions and trades in India. It is a state-level tax and has to be compulsorily paid by every staff member employed in private companies. The business owner is responsible for deducting professional Tax from his employees’ salaries and paying the amount collected to the appropriate government department.
Professional Tax is usually a slab amount based on the gross income of the professional. It is deducted from income every month. Some of the state governments have levied professional Taxes, and others didn’t. Professional Tax is a state-imposed tax and is imposed on income earned by employees on rendering their services. Witcorp Expert will help you get registered under Professional Tax without leaving the comfort of your home.
Service Covered
-
Issue of Enrolment/ Registration Certificate
-
Documented Follow-up
-
Business hours – CA support
-
Does not include PT payment
Who Should Buy
-
Every self employed professional
-
Any entity employing one or more employees
How It’s Done
-
Purchase of Plan
-
Upload documents on vault
-
Filing of enrolment/registration application
-
Receipt of enrolment certificate
Documents Required
-
Name, Contact Number and Email Id of Stakeholder.
-
Self Attested PAN, Aadhar & Passport size photo of Stakeholder.
-
Specimen Signatures of Stakeholder.
-
Latest Electricity Bill/Landline Bill of Registered Office.
-
NOC from owner of registered office. (If Owned)
-
Rent Agreement from Landlord. (If Rented/Leased)
-
PAN, TAN, COI of the Business Entity
-
Cancelled Cheque in business name
Which states fall under Professional Tax?
Professional Tax Applicable in States
-
Andhra Pradesh
-
Assam
-
Bihar
-
Chattisgarh
-
Gujarat
-
Karnataka
-
Kerala
-
Madhya Pradesh
-
Maharashtra
-
Manipur
-
Meghalaya
-
Mizoram
-
Orissa
-
Puducherry
-
Tamil Nadu
-
Tripura
-
West Bengal
Professional Tax Not Applicable in States
-
Arunachal Pradesh
-
Delhi
-
Goa
-
Haryana
-
Himachal Pradesh
-
Jammu & Kashmir
-
Jharkhand
-
Nagaland
-
Punjab
-
Rajasthan
-
Sikkim
-
Uttar Pradesh
-
Uttaranchal
-
Andaman & Nicobar
-
Chandigarh
-
Daman & Diu
-
Dadra & Nagar Haveli
-
Lakshadweep
What is Professional Tax and who Levies it?
The nomenclature ‘Professional tax’ could be one of those terms which do not completely convey the real meaning of the term. Unlike the name suggests, it is just not the tax levied only on professionals. It is a tax on all kinds of professions, trades, and employment and levied based on the income of such profession, trade and employment. It is levied on employees, a person carrying on business including freelancers, professionals, etc., subject to income exceeding the monetary threshold if any.
As per Article 246 of the Constitution of India, only Parliament has the exclusive power to make laws with respect to the Union List which includes taxes on income. The state has the power to make laws only with respect to the Concurrent and State list.
However, professional tax though is a kind of tax on income levied by State Government (not all states in the country chose to levy professional tax). The State Government is also empowered to make laws with respect to professional tax though being a tax on income under Article 276 of the Constitution of India which deals with tax on professions, trades, callings and employment.
It may be noted that professional tax is a deductible amount for the purpose of Income-tax Act, 1961 and can be deducted from taxable income.
Dual Registration and Separate Registration for Each State
An employer/professional must have dual registration. The two registrations required are:
-
A) Professional Tax Registration Certificate to pay tax on trade or profession
-
B) Professional Tax Enrollment Certificate to deduct such tax from the salaries, trade, etc.
For offices with multi-state presence, since the tax regimes vary in each state, a separate registration is required for each such office established under different State Legislations. Moreover, Registration Certificate has to be obtained by an employer within 30 days of the appointment of staff.
Deposit of Tax
|
Employer has employed |
Make payment within |
|
More than 20 Employees |
15 days from end of the month |
|
20 employees or less |
15th of next month from the end of each quarter |
Penalties for Non-Compliance:
While each state has the ability to fix penalty based on its own tax laws, the regime is generally centered around the following penalties:
|
Delay in |
Non-Compliance |
Penalty levied by most states |
|
Registration |
Non-registration when the employer was liable to be registered |
Rs 5/Day |
|
Payment |
Non-payment of tax or payment after the due date. |
10% of the Amount of Tax |
|
Filing of Return |
Non-filing of Tax Returns or delay in filing |
Rs 1000/ return delayed by 1 month Rs 2000/return for a further delay. |
Professional Tax Rate for Different States
Professional Tax or Profession Tax is levied by the State Government on the income of the assessee. Under Article 276 of the Indian Constitution, the state governments are empowered to decide the rate for the professional tax in the state. The maximum amount that can be charged under this tax regime is Rs. 2500. In a few states, this tax is even levied on the basis of source of income.
Professional Tax Rates in Andhra Pradesh
|
Slab (Income Per Month) |
Amount (Per Month) |
|
Up to Rs. 15,000 |
Nil |
|
Rs. 15,001 – Rs. 20,000/- |
Rs 150 |
|
Rs. 20, 001 or above |
Rs 200 |
Professional Tax Rates in Assam
|
Slab (Income Per Month) |
Amount (Per Month) |
|
Up to Rs.10,000/- |
Nil |
|
Rs. 10,001 to Rs. 15,000 |
Rs 175 |
|
Rs. 15,001 to Rs. 24,999/- |
Rs 180 |
|
Rs. 25,000 or above |
Rs. 208 |
Professional Tax Rates in Bihar
|
Slab (Income Per Month) |
Amount (Per Month) |
|
Up to Rs. 25,000/- |
Nil |
|
Rs. 25,001 – Rs. 41,666 |
Rs. 83.33 |
|
Rs. 41,667 – Rs. 83,333/- |
Rs. 166.67 |
|
Rs. 83,333 – or above |
Rs. 208.33 |
Professional Tax Rates in Goa
|
Slab (Income Per Month) |
Amount (Per Month) |
|
Up to Rs. 15,000/- |
Nil |
|
Rs. 15,001 – Rs.25,000/- |
Rs. 150 |
|
Rs. 25,001 or above |
Rs. 200 |
Professional Tax Rates in Gujarat
|
Slab (Income Per Month) |
Amount (Per Month) |
|
Up to Rs. 5,999/- |
Nil |
|
Rs. 6,000 – Rs. 8,999 |
Rs. 80 |
|
Rs. 9,000 – Rs. 11,999/- |
Rs. 150 |
|
Rs.12,000 or above |
Rs. 200 |
Professional Tax Rates in Jharkhand
|
Slab (Income Per Month) |
Amount (Per Month) |
|
Up to Rs. 25,000/- |
Nil |
|
Rs. 25,001 – Rs. 41,666/- |
Rs. 100 |
|
Rs. 41,667 – Rs. 66,666/- |
Rs. 150 |
|
Rs. 66,667 – Rs. 83,333/- |
Rs. 200 |
|
Rs. 83,334 – or above |
Rs. 208 (for first 11 months and Rs. 212 in last month) |
Professional Tax Rates in Karnataka
|
Slab (Income Per Month) |
Amount (Per Month) |
|
Up to Rs. 15,000/- |
Nil |
|
Rs. 15,001 or above |
Rs. 200 |
Professional Tax Rates in Kerala
|
Slab (Income Per Month) |
Amount (Per Month) |
|
Up to Rs. 1,999 |
Nil |
|
From Rs. 2,000 – Rs. 2,999 |
Rs. 20 |
|
From Rs. 3,000 – Rs. 4,999 |
Rs. 30 |
|
From Rs. 5,000 – Rs. 7,499 |
Rs. 50 |
|
From Rs. 7,500 – Rs. 9,999 |
Rs. 75 |
|
From Rs. 10,000 – Rs. 12,499 |
Rs. 100 |
|
From Rs. 12,500 – Rs. 16,666 |
Rs. 125 |
|
From Rs. 16,667 – Rs. 20,833 |
Rs. 166 |
|
Rs. 20,834 or above |
Rs. 208 |
Professional Tax Rates in Madhya Pradesh
|
Slab (Income Per Month) |
Amount (Per Month) |
|
Up to Rs. 18,750/- |
Nil |
|
Rs. 18,751 – Rs. 25,000/- |
Rs. 125 |
|
Rs. 25,001 – Rs. 33,333/- |
Rs. 167 |
|
Rs. 33,334/- or above |
208 (11 months) & 212 (12th month) |
Professional Tax Rates in Maharashtra
|
Slab (Income Per Month) |
Amount (Per Month) |
|
For Men |
Nil up to Rs. 7,500 |
|
From Rs. 7,500 – Rs. 10,000 |
Rs 175 |
|
For Women |
Nil up to Rs. 10,000 |
|
For all Above Rs. 10,000 |
Rs. 200 and Rs. 300 for the month of February |
Professional Tax Rates in Manipur
|
Slab (Income Per Month) |
Amount (Per Month) |
|
Up to Rs. 4,250/- |
Nil |
|
From Rs. 4,251 – Rs. 6,250/- |
Rs. 100 |
|
From Rs. 6,251 – Rs. 8,333/- |
Rs. 167 |
|
From Rs. 8,334 – Rs. 10,416/- |
Rs. 200 |
|
From Rs. 10,417 or above |
Rs. 208 & Rs. 212 |
Professional Tax Rates in Meghalaya
|
Slab (Income Per Month) |
Amount (Per Month) |
|
Up to Rs. 4,166/- |
Nil |
|
From Rs. 4,167 – Rs. 6,250/- |
Rs. 16.50 |
|
From Rs. 6,251 – Rs. 8,333/- |
Rs. 25 |
|
From Rs. 8,334 – Rs. 12,500/- |
Rs. 41.50 |
|
From Rs. 12,501 – Rs. 16,666/- |
Rs. 62.50 |
|
From Rs. 16,667 – Rs. 20,833/- |
Rs. 83.33 |
|
From Rs. 20,834 – Rs. 25,000/- |
Rs. 104.16 |
|
From Rs. 25,001 – Rs. 29,166/- |
Rs. 125 |
|
From Rs. 29,167 – Rs. 33,333/- |
Rs. 150 |
|
From Rs. 33,334 – Rs. 37,500 |
Rs. 175 |
|
From Rs. 37,501 – Rs. 41,666 |
Rs. 200 |
|
Above Rs. 41,667/- |
Rs. 208 |
Professional Tax Rates in Nagaland
|
Slab (Income Per Month) |
Amount (Per Month) |
|
Up to Rs. 4,000/- |
Nil |
|
From Rs. 4,001 – Rs. 5,000/- |
Rs. 35 |
|
From Rs. 5,001 – Rs. 7,000/- |
Rs. 75 |
|
From Rs. 7,001 – Rs. 9,000/- |
Rs. 110 |
|
From Rs. 9,001 – Rs. 12,000/- |
Rs. 180 |
|
From Rs. 12,001 or above |
Rs. 208 |
|
From Rs. 25,001 – Rs. 29,166/- |
Rs. 125 |
|
From Rs. 29,167 – Rs. 33,333/- |
Rs. 150 |
|
From Rs. 33,334 – Rs. 37,500 |
Rs. 175 |
|
From Rs. 37,501 – Rs. 41,666 |
Rs. 200 |
|
Above Rs. 41,667/- |
Rs. 208 |
Professional Tax Rates in Odisha
|
Slab (Income Per Month) |
Amount (Per Month) |
|
Up to Rs. 13,304/- |
Nil |
|
From Rs. 13,305 – Rs. 25,000/- |
Rs. 125 |
|
From Rs. 25,001 or above |
Rs. 200 (11 months) & Rs. 300 (12th month) |
|
From Rs. 15,001 – Rs. 25,000 |
Rs. 130 |
|
From Rs. 25,001 – Rs. 40,000 |
Rs. 150 |
|
Over and Above Rs. 40,000 |
Rs. 200 |
Professional Tax Rates in Puducherry
|
Slab (Income Per Month) |
Amount (Per Month) |
|
Up to Rs. 16,666/- |
Nil |
|
From Rs. 16,667 – Rs. 33,333/- |
Rs. 41.66 |
|
From Rs. 33,334 – Rs. 50,000/- |
Rs. 83.33 |
|
From Rs. 50,001 – Rs. 66,666/- |
Rs. 125 |
|
From Rs. 66,667 – Rs. 83,333 |
Rs. 166.67 |
|
Rs. 83,333 and above |
Rs. 208.33 |
Professional Tax Rates in Punjab
|
Slab (Income Per Month) |
Amount (Per Month) |
|
Above Rs. 20,833/- |
Rs. 200 |
Professional Tax Rates in Sikkim
|
Slab (Income Per Month) |
Amount (Per Month) |
|
Up to Rs. 20,000/- |
Nil |
|
From Rs. 20,001 – Rs. 30,000/- |
Rs. 125 |
|
From Rs. 30,001 – Rs. 40,000/- |
Rs. 150 |
|
Above Rs. 40,000 |
Rs. 200 |
Professional Tax Rates in Telangana
|
Slab (Income Per Month) |
Amount (Per Month) |
|
Up to Rs. 15,000/- |
Nil |
|
From Rs. 15,001 – Rs. 20,000/- |
Rs. 150 |
|
From Rs. 20,001 – or above |
Rs. 200 |
Professional Tax Rates in Tripura
|
Slab (Income Per Month) |
Amount (Per Month) |
|
Up to Rs. 7,500/- |
Nil |
|
From Rs. 7,501 – Rs. 15,000/- |
Rs. 150 |
|
Rs. 15,000 or above |
Rs. 208 |
Professional Tax Rates in West Bengal
|
Slab (Income Per Month) |
Amount (Per Month) |
|
Up to Rs. 8,500 |
Nil |
|
From Rs. 8,501 – Rs. 10,000 |
Rs. 90 |
|
From Rs. 10,001 – Rs. 15,000 |
Rs. 110 |
|
From Rs. 15,001 – Rs. 25,000 |
Rs. 130 |
|
From Rs. 25,001 – Rs. 40,000 |
Rs. 150 |
|
Over and Above Rs. 40,000 |
Rs. 200 |
Professional Tax Rates in Tamil Nadu
|
Slab (Income Per Month) |
Amount (Per Month) |
|
Up to Rs. 21,000 |
Nil |
|
From Rs. 21,001 – Rs. 30,000 |
Rs. 100 |
|
From 30,001 – Rs. 45,000 |
Rs. 235 |
|
From Rs. 40,001 – Rs. 60,000 |
Rs. 510 |
|
From Rs. 60,001 – Rs. 75,000 |
Rs. 760 |
|
From Rs. 75,001 and above |
Rs. 1095 |
Similarly, there are different slabs and rates for the other states as well. For the month of February, the Professional Tax is a little higher than the rest of the eleven months in the year.
Who is responsible to collect and pay professional tax?
-
Professional tax is collected by the Commercial Tax Department. The commercial tax department of the respective states collect it which ultimately reaches the fund of municipality corporation.
Persons responsible to pay professional tax
What is the procedure to pay Professional Tax? Is any return to be filed?
This is again a State-specific query. However, in general, a professional tax may be paid either online/offline. Further, depending on the State’s requirement, professional tax returns also need to be filed at specified intervals.
Consequences of Violation of Professional Tax Regulation
While the actual amount of penalty or penal interest may depend on the respective State’s legislation, a penalty may be levied by all such states for not registering once professional tax legislation becomes applicable.
Further, there are also penalties for not making the payment within the due date and also failing to file the return within the specified due date.
For example: In the State of Maharashtra Rs 5/day is imposed as a penalty for delay in registration, Interest @ 1.25% per month of delay in payment, a penalty of 10% of the amount of tax in case of delay/non payment of professional tax, Rs 1000 – Rs 2000 penalty for delay in filing the return
Due Dates for Filing of Professional Tax Returns in India
In India, Professional Tax Payment Due Dates are listed by state, (List Cant Be Seen in Mobile)
|
S No |
State |
Periodicity |
Professional Tax Payment Due Date |
|
1 |
Andhra Pradesh |
Monthly |
It is always the 10th of the month |
|
2 |
Assam |
Monthly |
Usually on the 28th of each month |
|
3 |
Bihar |
Yearly |
The 30th of November is always the same |
|
4 |
Gujarath |
Monthly |
On the 15th of each month |
|
5 |
Jharkhand |
Yearly |
Every year on October 31st |
|
6 |
Karnataka |
Monthly |
Every month on the 20th |
|
7 |
Kerala |
Half Yearly |
28th of February and 31st of August |
|
8 |
Madhya Pradesh |
Monthly |
Every 10th of the month |
|
9 |
Maharashtra |
Monthly |
On the last day of every month |
|
10 |
Manipur |
Yearly |
Taking place on the 30th of March |
|
11 |
Meghalaya |
Monthly |
Every 28th of the month |
|
12 |
Odisha |
Monthly |
On the last day of every month |
|
13 |
Mizoram |
Yearly |
On June 30th |
|
14 |
Puducherry |
Half Yearly |
The 30th of June and the 31st of December |
|
15 |
Sikkim |
Quarterly |
The 31st of July, the 31st of October, the 31st of January, and the 30th of April |
|
16 |
Tamil Nadu |
Half Yearly |
On the 30th of September and the 31st of March |
|
17 |
Telangana |
Monthly |
Every 10th of the month |
|
18 |
West Bengal |
Monthly |
Every 21st of the month |
Frequently Asked questions
1.What is professional tax and when is it levied?
Professional tax is a state level tax which is imposed on income earned by way of profession, trade, calling or employment. The tax is based on slabs depending upon income of individual who may be self employed or working as employee of an entity. At present the maximum tax that can be imposed is restricted to is Rs. 2,500/-
2.Is there any exemption from PT payment?
Every state has its own governing provisions and exemption criteria. For example Karnataka PT act, has given exemption to certain persons from payment of PT. All charitable and philanthropic hospitals or nursing homes situated in places below the Taluk level in all districts of the State except Bangalore and Bangalore Rural District. Directors of Companies registered in Karnataka and nominated by the financing agencies owned or controlled by the State Government or by other statutory bodies. Foreign technicians employed in the State provided their appointments are approved by the Government of India for the purpose of exemption from payment of income tax for the said period ( exemption is for a period of 2 years from the date of their joining duty). Combatant and civilian non combatant members of the Armed Forces who are governed by the Army Act, the Navy Act and the Air Force Act. Salaried or wage earning blind persons. Salaried or wage earning deaf and dumb persons. Holders of permits of single taxi or single three wheeler goods vehicle. Institutes teaching Kannada or English Shorthand or Typewriting. A Physically handicapped person not less than 40% of permanent disability (subject to production of certificate from the HOD of Government Civil Hospital). An ex-serviceman not falling under Sl No.1 of the Schedule. A person having single child and who has undergone sterilization operation, subject to production of a certificate from the District Surgeon, Government Civil Hospital, for having undergone such operation. Central Para Military Force (CPMF) Personnel. Persons running educational institutions in respect of their branches teaching classes up to twelfth standard or pre-University Education. No tax is payable by persons who have attained age of sixty five years. Also no tax is payable for holding any Profession for less than 120 days in the year. Our experts will guide on on applicability of the provisions
3.Is Professional tax imposed in every state in India?
Professional tax is imposed only in following States: Karnataka, Bihar, West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Maharashtra, Tamilnadu, Gujarat, Assam, Kerala, Meghalaya, Odisha, Tripura, Madhya Pradesh, and Sikkim.
4.Can the professional tax liability amount be paid in lump sum?
In certain states there is concept of composition scheme. For e.g. in case of Maharashtra, the government announced composition scheme under which any person liable to make payment to government at rate of Rs. 2500 may make a lump sum payment in advance of Rs. 10,000 and his liability to pay for 5 years will be discharged.
5.What will be the other costs in the registration process?
The plan price covers all professional fees and convenience charge. Since Professional tax is state level tax the applicable govt. charges vary from state to state.
Government charges will be charged on actual basis.
6.Which are the specific cities where the service will be delivered?
The service is state specific in case you need a shop license and will be rendered only in specific cities being Mumbai, Gurgaon, Hyderabad, Kolkata, Jaipur, Surat, Bangalore, Chandigarh, Pune and Delhi
7.Who is responsible for deducting the tax and depositing the same with Government?


8.What is enrolment certificate and what is registration certificate?
Every employer in specific states is required to deduct taxes from salary when paid to one or more employees when payment made exceeds Rs.5,000/- (this limit is for Maharashtra) and deposit with state government. That entity is required to obtain registration certificate. When person is employed in profession by two or more employers and is getting salary/wages exceeding Rs.5,000/- but employer is not deducting professional tax then the individual needs to get enrolment certificate from authority.
Legal Services
Businesses operate in a very dynamic environment. Right from inception, a business transacts with numerous stakeholders who can be co-founders, customers, business partners, vendors, investors among others, our Legal experts will understand your case and draft documents/ agreements defining all terms, conditions and legal recourse that can be opted for on being breached. Avoid any legal hassles by getting your documents drafted by our professionals.
Documentation Services
Get your Legal Documentations such as Agreements, Contracts, Offer Letters, Termination Letter, Government Notices response or any related documents prepared or verified by the experts to avoid any legal complications or troubles at later stage, from Employees to Vendors or Stakeholders.
Valuation Services
We provide valuation support to our clients engaged in merger and acquisition activities. Leveraging on our industry knowledge held by our industry specialists, we not only take into account characteristics which are specific to a particular industry or country but also the strategic objectives our clients have for the particular transaction.
Certification & Attestation
Certifications of professionals are required for various purposes such as Banking, Visa, Wealth Certification or even opening of Current Account with the Banks. Get any valid and legal documents certified by the professionals and move ahead of others to get it done.
Legal Documentation Services
- Legal Agreements
- Business Agreements
- Daily Business Agreements
- Corporate Agreements
Frequently Asked Questions
Who are the professionals who will be drafting the legal documents?
Team Witcorp has its own expert team of legal consultants, property experts and tax experts. Our team of Chartered Accountants, Company Secretaries, Advocates and other legal consultants brings with them years of experience in their respective domains of specialisation.
Do all agreements need to be notarised? Is stamp duty to be paid on every legal document?
Some documents such as Real Estate property deed need to be notarised where the documents are presented in front of a notary designated person. Such documents can be enforced in court of law only if they have been notarised and stamp duty of appropriate value has been paid. Some states allow e-stamping too.
There are some agreements and other legal documents that need not be acknowledged before a notary public unless specifically required by state or municipal law.
Under the plan our experts will prepare a draft which will be shared with you. Make sure you share all your specifications and expectations and review the draft carefully. At end of process you will receive a soft copy of final draft which you may use as need be. We do not cover notary and stamp duty charges in this package.
Which legal documents should be reviewed?
Legal documents define the scope of engagement and roles and responsibilities along with privileges of the concerned parties. These documents contain clauses may have implications and need to be read carefully before signing as on signing you become legally bound by the contract.
Any new legal document with the potential to have a substantial impact on your finances, time or responsibilities should be reviewed. Any time you make changes to a legal document or your situation changes, a legal document review is a good idea to ensure your interests are protected
Why should the documents be reviewed?
Having your legal documents or contract reviewed by an expert before you sign ensures your interests are protected. Any new legal document with the potential to have a substantial impact on your finances, time or responsibilities should be reviewed. Document review is also recommended any time you make changes to a legal document or your situation changes. Witcorp legal document review services are available for an affordable price that includes document review or contract review by an attorney who understands the language used in legal documents.
Which legal documents will be reviewed under the plan?
Your attorney can review any contract, agreement or document you choose, including those that don’t require your signature. If any additional special review is needed, your attorney will advise you.
Do I need to share any other documents too?
While reviewing the document, the experts may ask for more details to cover all the aspects of the contract or the deed. The additional documents required shall vary from case to case and will be communicated by the expert.